Robot Setup#
We provide details about setting up the Galaxea R1 robot, including the installation of cameras and necessary software packages.
Hardware Installation#
We install our robot with the following items:
2x ZED Mini cameras (wrist cameras);
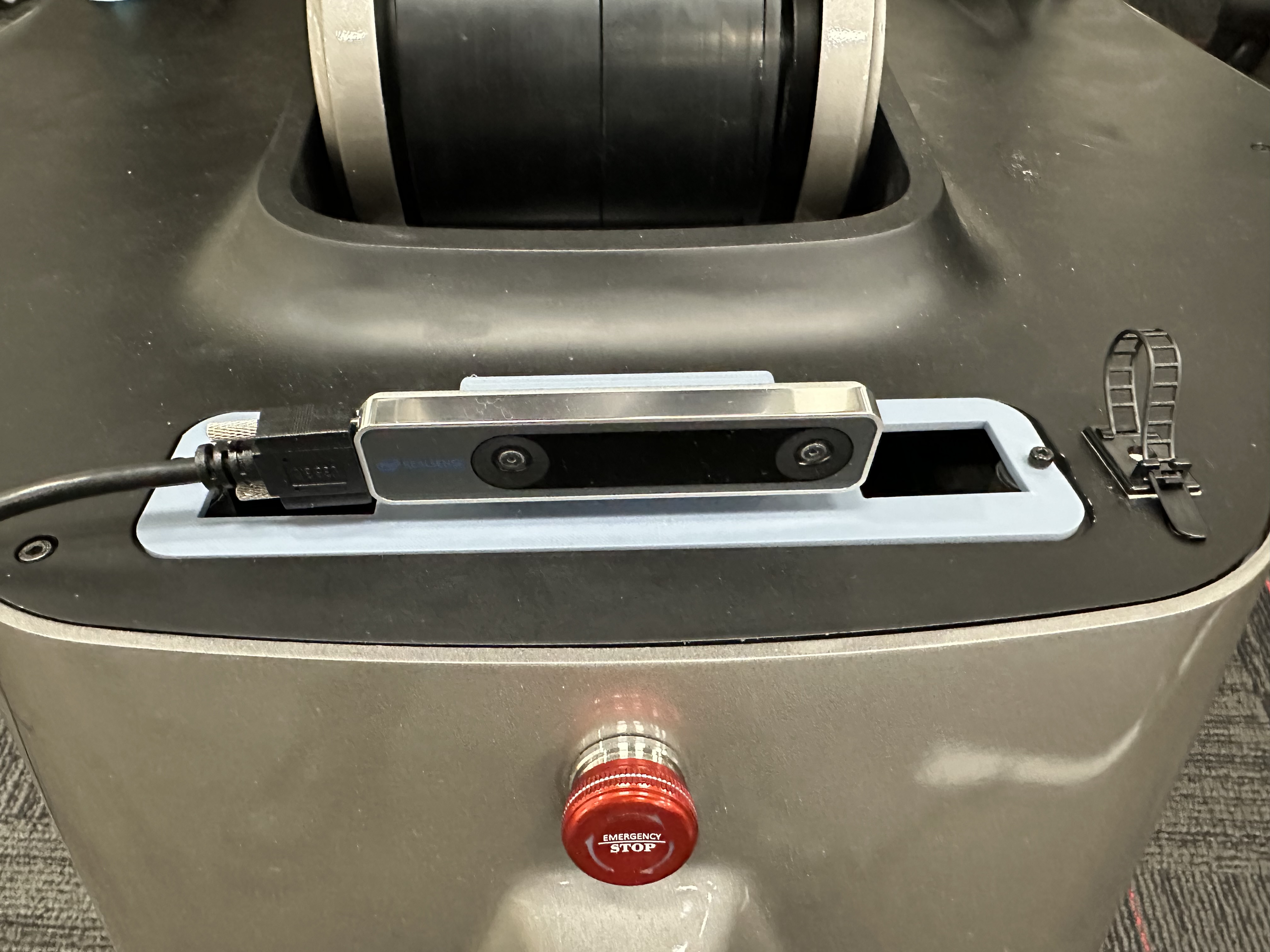
1x Intel RealSense T265 tracking camera (visual odometry);
1x SABRENT USB 3.0 hub.
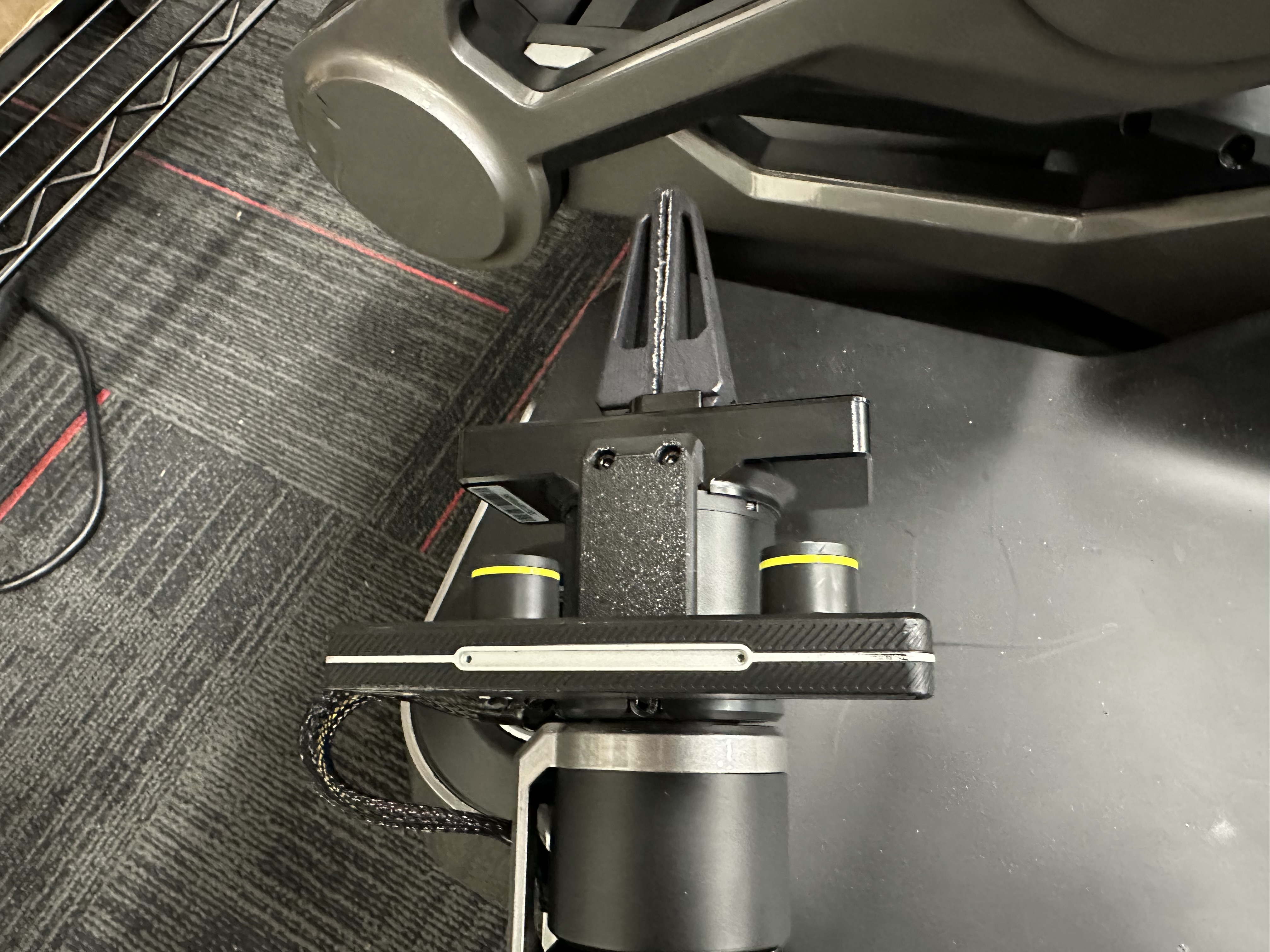
We also designed 3D-printable mounts for the cameras:
First connect the USB hub to the robot’s onboard computer. This step requires the robot’s body shells to be removed.
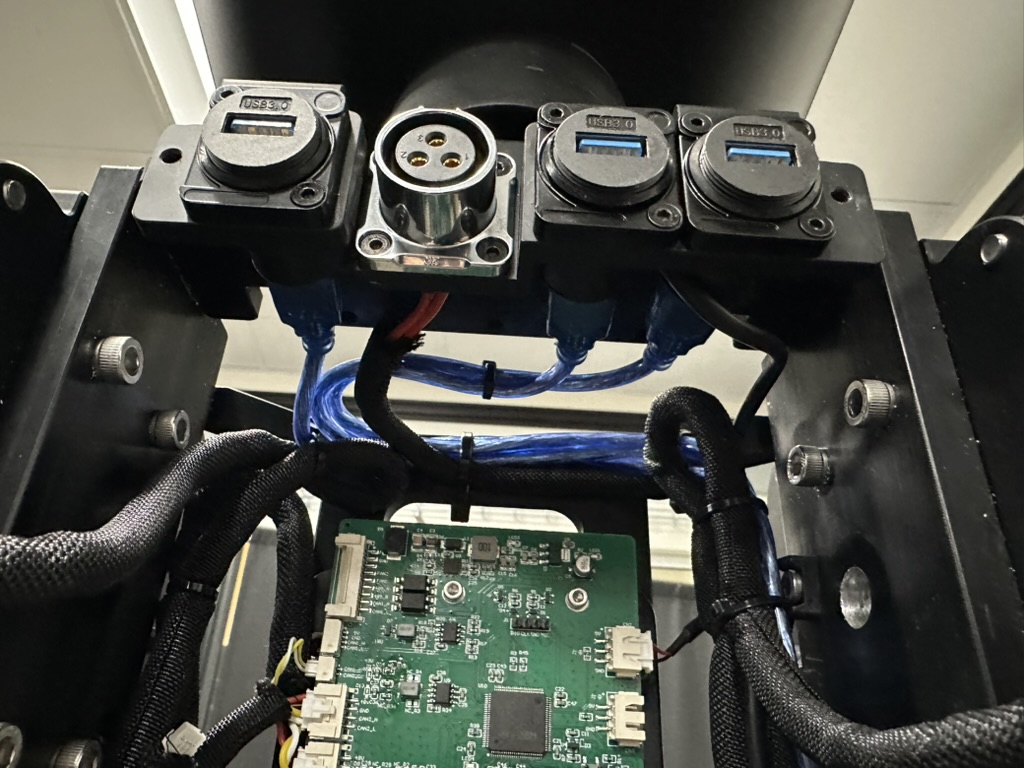


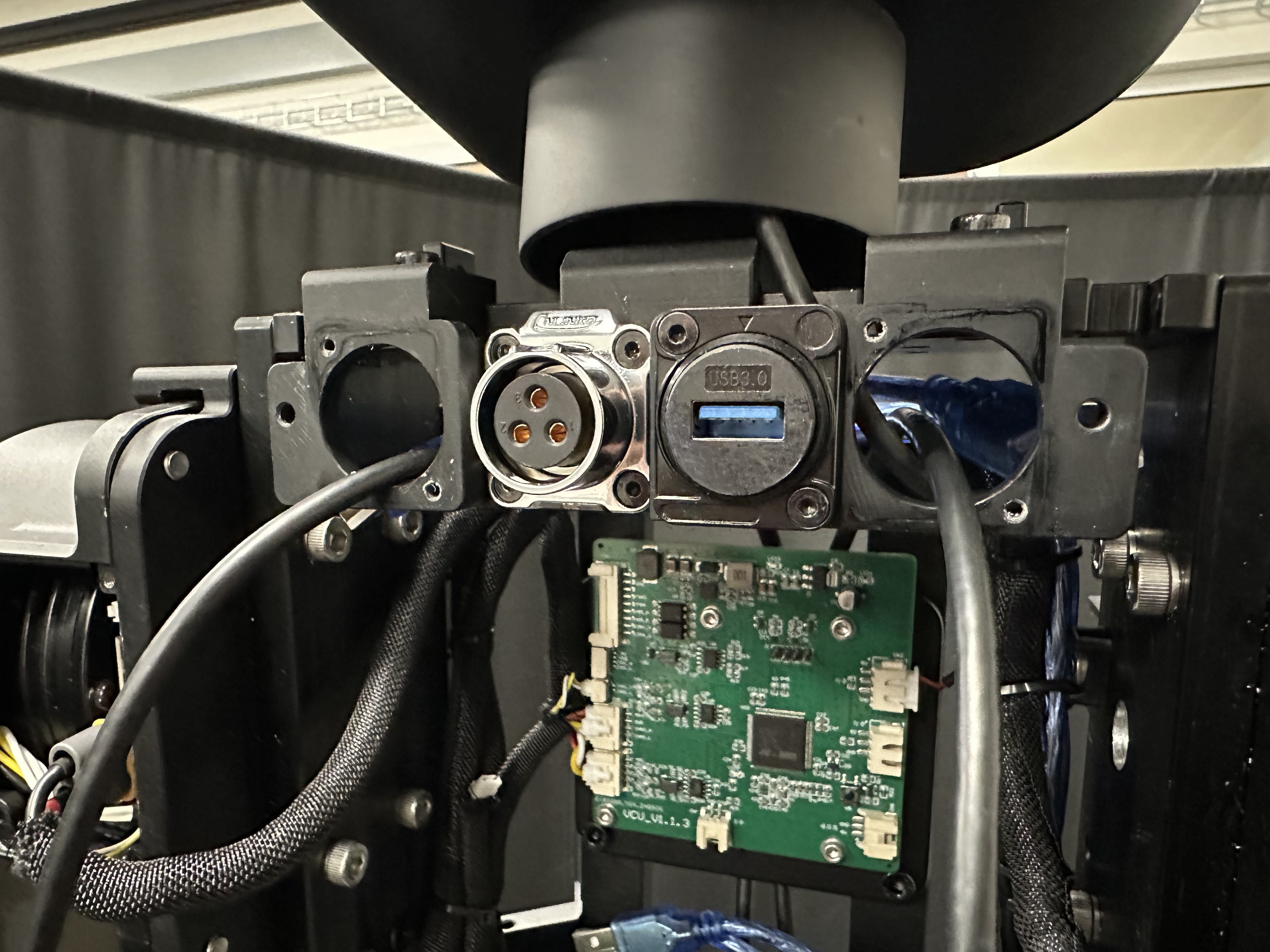
Then attach the USB hub to the robot’s back. The USB hub is later used for camera connections and the push buttons are convenient for connecting/disconnecting the cameras.
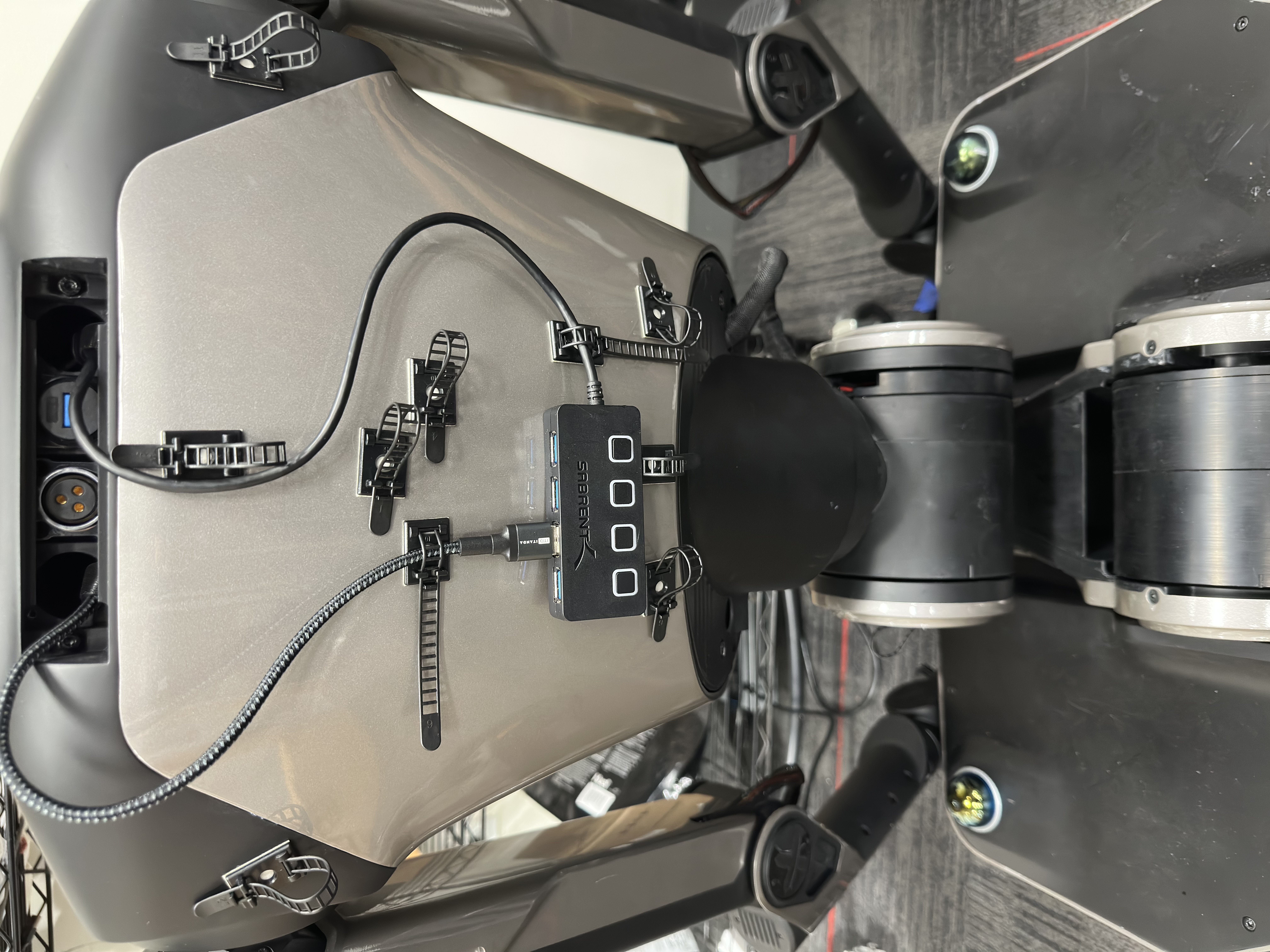
Install cameras on the robot using provided mounts.




Robot Connection#
Wireless Connection#
To connect the robot wireless, make sure both the robot and the workstation are connected to the same WiFi.
We then need to find the robot’s IP address by running ifconfig mlan0 on the robot computer.
For example, the IP address for our robot is 10.5.6.145 and the user name is nvidia.
We can ssh into the robot onboard computer by running ssh nvidia@10.5.6.145.
Wired Connection#
First, use an Ethernet cable to physically connect the robot and the workstation.
Next, find the connected Ethernet interface on the workstation by running ifconfig. The output looks like:
docker0: ...
enp37s0f0: ...
enp37s0f1: ...
lo: ...
en* are the Ethernet interfaces. Identify the physically connected one (e.g., enp37s0f1). Then run sudo ip ad add 10.0.0.10/24 dev enp37s0f1 on the workstation. This assigns a static IP address to the workstation. To check this is successful, run ip a l, you should see something like:
3: enp37s0f1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 10.0.0.10/24 scope global enp37s0f1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Now move to the robot onboard computer and open a terminal, first run ip a l to find the Ethernet interface. You will see:
...
6: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
altname enP5p1s0f1
...
Note that the physically connected interface is eth1. Take a note of its full name (e.g., enP5p1s0f1). Then run sudo ip ad add 10.0.0.20/24 dev enP5p1s0f1. This assigns the same static IP address to the robot (effectively with mask 255.255.255.0). To verity this is successful, run ip a l again and you should see:
6: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
altname enP5p1s0f1
inet 10.0.0.20/24 scope global eth1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
To test, from the workstation, run ping 10.0.0.20. You should see:
PING 10.0.0.20 (10.0.0.20) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.0.0.20: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.273 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.20: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.196 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.20: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.199 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.20: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.249 ms
...
Conversely, you can test from the robot onboard computer by running ping 10.0.0.10.
Software Installation#
Install brs_ctrl on Robot Computer#
First we need to install brs_ctrl on the robot onboard computer.
Follow the instructions in Create Environment and Install brs_ctrl.
Note
If rospy.init_node is hanging on the robot computer, replace /opt/ros/noetic/lib/python3/dist-packages/rosgraph/roslogging.py with this file.
Build ZED ROS Wrapper#
Follow the instructions here to build the ZED ROS wrapper from source on the robot onboard computer.
After building the ROS package, to use our camera config, copy launch files multicam_single_nodelet.launch behavior-robot-suite/brs-ctrl to PATH_TO_ROS_WORKSPACE/src/zed-ros-wrapper/zed-wrapper/launch/, and nodelet_mod.launch behavior-robot-suite/brs-ctrl to PATH_TO_ROS_WORKSPACE/src/zed-ros-wrapper/zed-wrapper/launch/include/.
Be sure to change camera serial numbers in multicam_single_nodelet.launch to match your cameras.
camera_sn_1 corresponds to the head camera.
camera_sn_2 corresponds to the left wrist camera.
camera_sn_3 corresponds to the right wrist camera.
77 ...
78 <!-- Base frame -->
79 <arg name="base_frame_1" default="base_link" />
80
81 <arg name="camera_sn_1" default="20209960" />
82 <arg name="gpu_id_1" default="-1" />
83
84 <!-- LEFT WRIST CAMERA -->
85 <arg name="camera_name_2" default="zed2_left_wrist" />
86 <arg name="camera_model_2" default="zedm" /> <!-- 'zed' or 'zedm' or 'zed2' -->
87 <arg name="zed_nodelet_name_2" default="zed_nodelet_left_wrist" />
88 <arg name="point_cloud_freq_2" default="60" />
89 <arg name="pub_frame_rate_2" default="60" />
90 <arg name="grab_resolution_2" default="VGA" />
91 <arg name="grab_frame_rate_2" default="60" />
92 <arg name="depth_mode_2" default="PERFORMANCE" />
93 <arg name="min_depth_2" default="0.1" />
94 <arg name="max_depth_2" default="1" />
95
96 <!-- Base frame -->
97 <arg name="base_frame_2" default="base_link" />
98
99 <arg name="camera_sn_2" default="19966609" />
100 <arg name="gpu_id_2" default="-1" />
101
102 <!-- RIGHT WRIST CAMERA -->
103 <arg name="camera_name_3" default="zed2_right_wrist" />
104 <arg name="camera_model_3" default="zedm" /> <!-- 'zed' or 'zedm' or 'zed2' -->
105 <arg name="zed_nodelet_name_3" default="zed_nodelet_right_wrist" />
106 <arg name="point_cloud_freq_3" default="60" />
107 <arg name="pub_frame_rate_3" default="60" />
108 <arg name="grab_resolution_3" default="VGA" />
109 <arg name="grab_frame_rate_3" default="60" />
110 <arg name="depth_mode_3" default="PERFORMANCE" />
111 <arg name="min_depth_3" default="0.1" />
112 <arg name="max_depth_3" default="1" />
113
114 <!-- Base frame -->
115 <arg name="base_frame_3" default="base_link" />
116
117 <arg name="camera_sn_3" default="18204585" />
118 ...
Build RealSense SDK for T265#
Because our visual odometry the T265 camera requires an old version of RealSense SDK, we build it from source. First, download RealSense SDK 2.43.0 and unzip it.
wget https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/archive/refs/tags/v2.43.0.zip
unzip v2.43.0.zip
cd into the directory, create a directory called build, and cd into it
cd librealsense-2.43.0
mkdir build && cd build
Run the CMake command:
cmake ../ -DFORCE_RSUSB_BACKEND=ON -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=release -DBUILD_WITH_CUDA:bool=true
Still in the build directory. Run make -j4 and then sudo make install. Now the SDK is installed.